Elements of Data Science
SDS 322E
Department of Statistics and Data Sciences
The University of Texas at Austin
Fall 2025
Learning objectives
| Item | Package | Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Training-testing split | rsample | initial_split(), training(), testing() |
| Set up a pre-processing recipe | recipes | recipe(), step_*(), all_predictors() |
| Set up a model | parsnip | linear_reg(), logistic_reg(), nearest_neighbor(), set_engine() |
| Set up a model workflow | workflows | workflow(), add_recipe(), add_model() |
| Fit a model | infer / rsample | fit(), vfold_cv(), fit_resamples(), collect_metrics() |
| Extract the model output | broom | glance(), tidy(), augment() |
| Calculate model metrics | yardstick | metrics(), conf_mat(), roc_curve(), autoplot() |
Roadmap
- Example #1: A basic linear model
- Your time: apply the workflow for logistic regression
- Example #2: Add the training-testing split for logistic regression
- Your time: apply the training-testing split for KNN classification
- Example #3: Add cross-validation for KNN classification
- Example #4: Add hyper-parameter tuning with cross-validation for KNN classification
Follow along the class example with
usethis::create_from_github(SDS322E-2025Fall/1103-tidymodels")
Example #1 : linear model
Step 1: Specify the model:
Step 2: Specify the pre-processing steps:
Step 3: Build a workflow:
Step 4: Fit the model:
Step 5: Predict:
Step 6: Calculate classification metrics:
Your time
Can you replicate the example to fit a logistic regression?
- Step 1: you will be using the
lgoistic_reg(), which engine to use?
- Step 2: preprocessing
- Step 3: build a workflow to combine the model and recipe
- Step 4: fit the model
- Step 5: obtain the prediction
- Step 6: obtain the accuracy metric.
If you have extra time,
- read the documentation of the function
conf_mat()and obtain the confusion matrix - read the documentation of the function
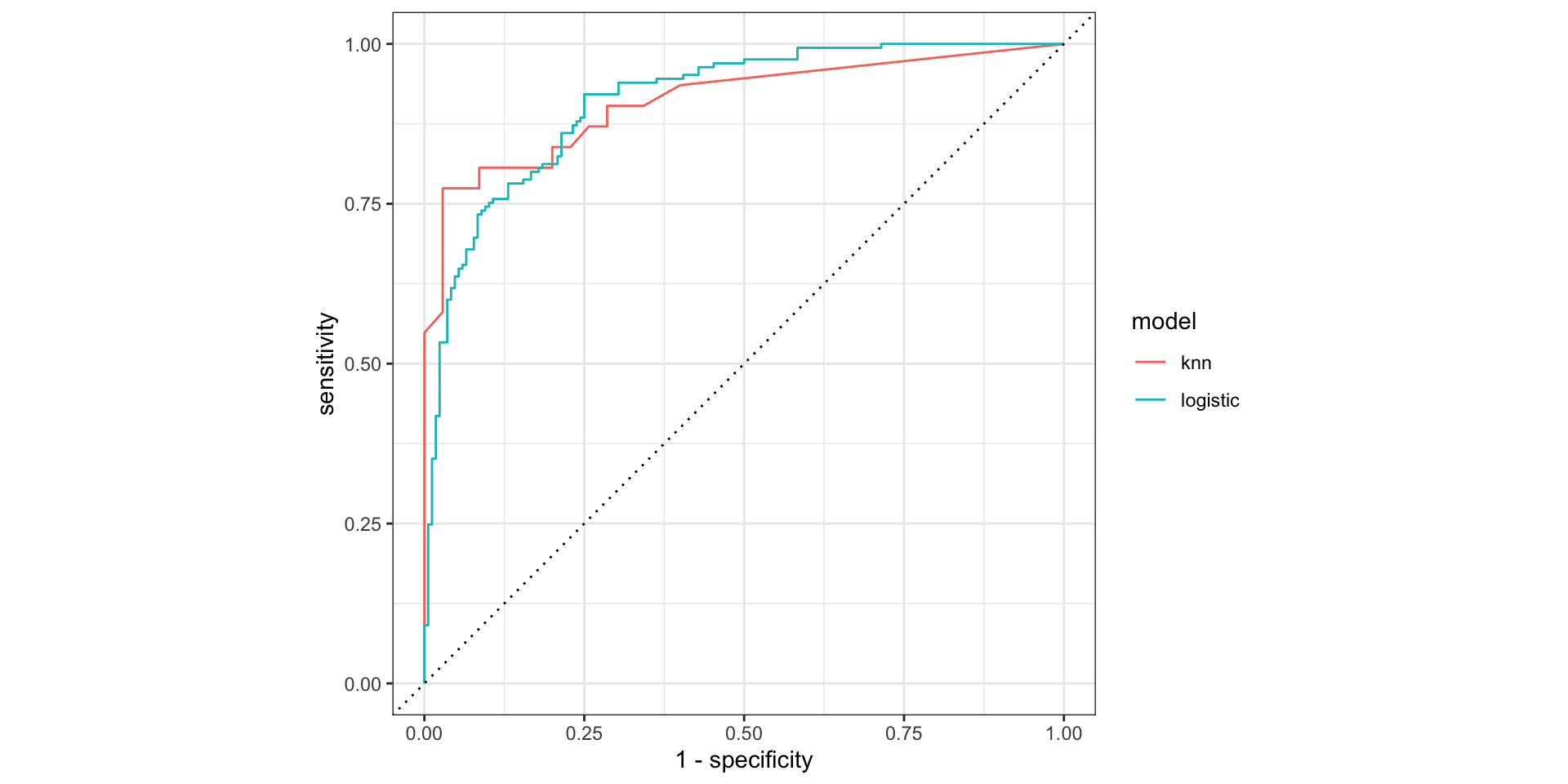
roc_curve()and plot the ROC curve
Solution
Step 1: Specify the model:
Step 2: Specify the preprocessing step:
Step 3: Build a workflow:
Step 4: Fit the model:
Step 5: Predict:
Solution
Step 6: Obtain accuracy measures:
More metrics calculated in the wild:
Example #2: Add training-testing split
Step 0: Training-testing split: new
Step 1/2/3: Specify the model/pre-processing recipe/workflow:
lr_mod <- parsnip::logistic_reg() %>% parsnip::set_engine("glm")
lr_rec <- recipes::recipe(sex ~ flipper_len + bill_len + bill_dep, data = penguins_train) |>
recipes::step_naomit(recipes::all_predictors())
lr_wf <- workflows::workflow() |> workflows::add_recipe(lr_rec) |> workflows::add_model(lr_mod)Step 4: Fit the model: train on the training data
Step 5: Predict: predict on the testing dataset
Example #2: Add training-testing split
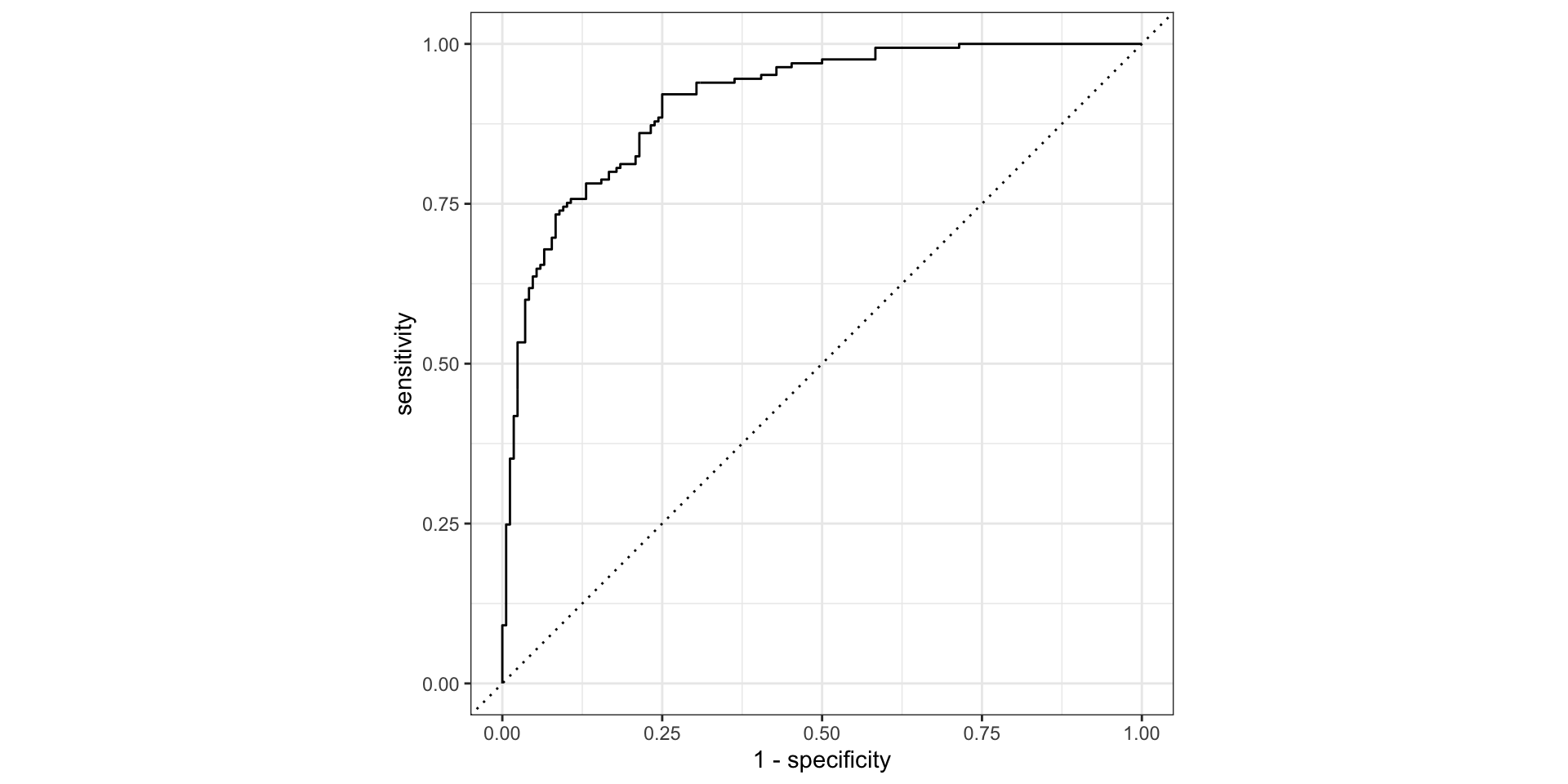
Step 6: Calculate classification metrics:
Your time: construct a KNN classification model with training-testing split
Step 0: training-testing split
Step 1: Specify the model:
- Can you find which model function to use for KNN classification? Which mode? Do you know where to specify the number of neighbors? We will be using the
kknnengine
Step 2: Specify the pre-processing recipe:
- In KNN, we need to scale the variables (since it is a distance based algorithm) - can you find the correct place to add the scaling step?
Step 3: Construct a workflow to combine the recipe and the model
Step 4: Fit the model on the training data
Step 5: Predict on the testing data
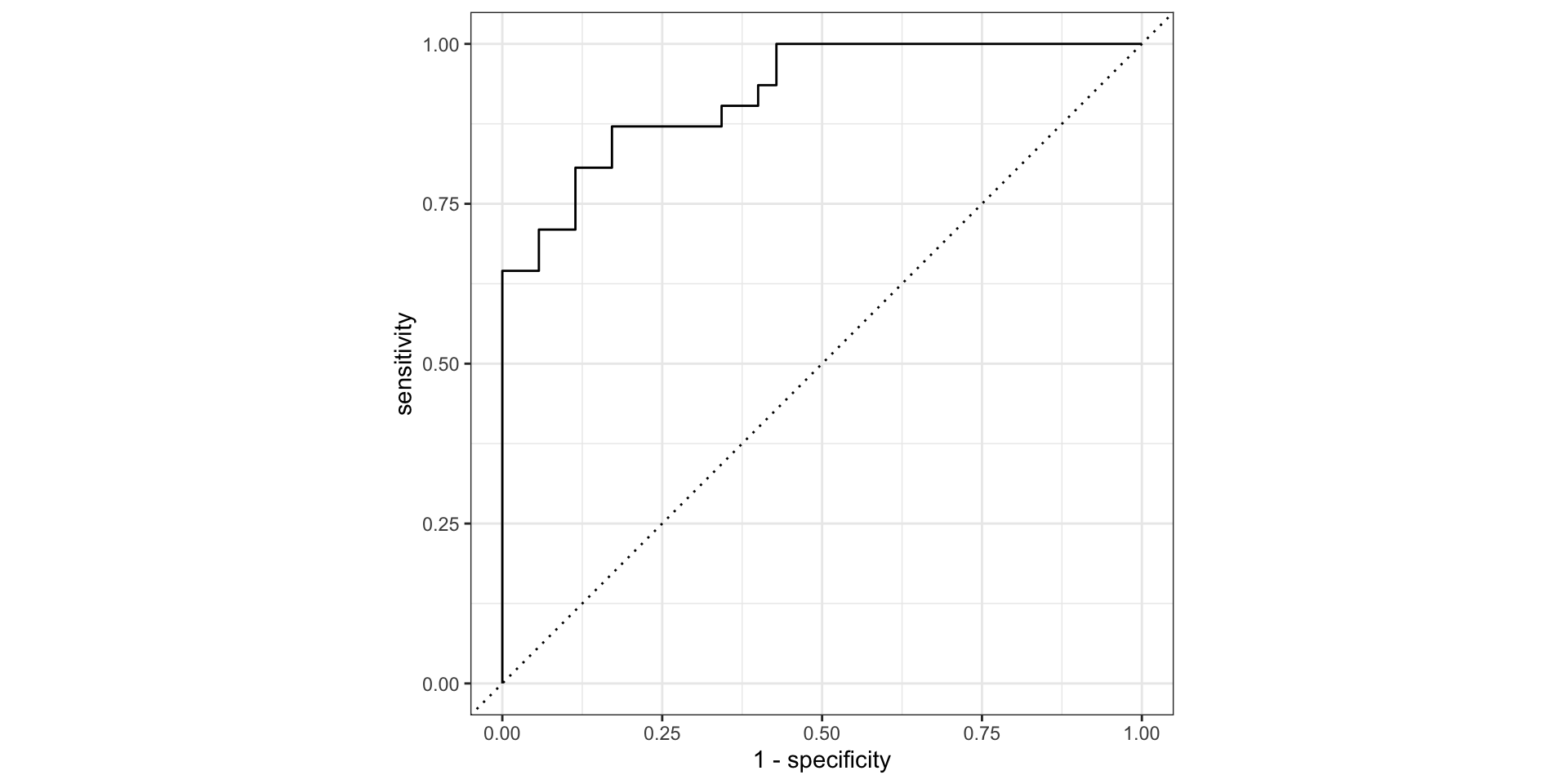
Step 6: Calculate accuracy metrics
Solution
Step 0: training-testing split:
Step 1: Specify the pre-processing recipe: new
Step 2: Specify the model:
You can also write it as:
Model parameters, e.g. neighbors = 7, are always specified within the model, nearest_neighbor() - we will look at more complicated cases on how to tune this parameter later.
Solution
Step 3: Build a workflow:
Step 4: Fit the model:
Example: Cross validation with KNN
Step 1: Specify the model
Step 2: Specify the pre-processing recipe
Step 3: Build a workflow
Step 4: Fit the model
Generate the cross validation sampling
Fit the model on the folds
Step 5/6: Predict and calculate classification metrics
Example #3: Cross validation with KNN
Step 1/2/3: Specify the pre-processing recipe, the model, and the workflow - same
penguins_clean <- datasets::penguins |> na.omit()
set.seed(123)
penguins_split <- rsample::initial_split(penguins_clean, prop = 0.8)
penguins_train <- rsample::training(penguins_split)
penguins_test <- rsample::testing(penguins_split)
penguins_rec <- recipe(sex ~ bill_len + bill_dep + flipper_len, data = penguins_train) |>
step_normalize(all_predictors())
knn_mod <- nearest_neighbor(mode = "classification", neighbors = 7) |> set_engine("kknn")
wf <- workflow() |> add_recipe(penguins_rec) |> add_model(knn_mod)Step 4: Generate the cross validation sampling/ Fit the model
penguins_folds <- rsample::vfold_cv(penguins_train, v = 10)
cv_res <- fit_resamples(wf, resamples = penguins_folds)
cv_res |> collect_metrics()# A tibble: 3 × 6
.metric .estimator mean n std_err .config
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <chr>
1 accuracy binary 0.865 10 0.0151 Preprocessor1_Model1
2 brier_class binary 0.0987 10 0.00930 Preprocessor1_Model1
3 roc_auc binary 0.936 10 0.0128 Preprocessor1_Model1Example #3: Cross validation with KNN
# A tibble: 3 × 4
.metric .estimator .estimate .config
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
1 accuracy binary 0.778 Preprocessor1_Model1
2 roc_auc binary 0.868 Preprocessor1_Model1
3 brier_class binary 0.138 Preprocessor1_Model1The accuracy metrics here is the average of the 10 folds:
# A tibble: 3 × 6
.metric .estimator mean n std_err .config
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <chr>
1 accuracy binary 0.865 10 0.0151 Preprocessor1_Model1
2 brier_class binary 0.0987 10 0.00930 Preprocessor1_Model1
3 roc_auc binary 0.936 10 0.0128 Preprocessor1_Model1Step 5: Predict
Example #4: hyper-parameter tuning with CV
Cross validation is more useful for hyper-parameter tuning - e.g. choosing the best number of neighbors in KNN.
Step 1: Specify the model
Step 2: Specify the pre-processing recipe
Step 3: Build a workflow
Step 4: Fit the model
- Generate the cross validation sampling
- Generate the hyperparameter grid
- Fit the model on the cv folds and hp grid
- Find the best model
Step 5/6: Predict and calculate classification metrics
Example #4: hyper-parameter tuning with CV
Step 1/2/3: Specify the pre-processing recipe, the model, and the workflow - same
penguins_clean <- datasets::penguins |> na.omit()
set.seed(123)
penguins_split <- initial_split(penguins_clean, prop = 0.8)
penguins_train <- training(penguins_split)
penguins_test <- testing(penguins_split)
penguins_rec <- recipe(sex ~ bill_len + bill_dep, data = penguins_train) |>
step_normalize(all_predictors())
knn_spec <- nearest_neighbor(mode = "classification", neighbors = tune::tune()) |> set_engine("kknn")
knn_wf <- workflow() |> add_recipe(penguins_rec) |> add_model(knn_spec) Step 4: Generate the cross validation sampling
penguins_folds <- vfold_cv(penguins_train, v = 10)
knn_grid <- dials::grid_regular(dials::neighbors(range = c(1, 20)), levels = 20)
# rather than using `fit_resamples()` we use `tune_grid()`
knn_res <- tune::tune_grid(knn_wf, resamples = penguins_folds, grid = knn_grid)
head(knn_res, 3)# A tibble: 3 × 4
splits id .metrics .notes
<list> <chr> <list> <list>
1 <split [239/27]> Fold01 <tibble [60 × 5]> <tibble [1 × 3]>
2 <split [239/27]> Fold02 <tibble [60 × 5]> <tibble [1 × 3]>
3 <split [239/27]> Fold03 <tibble [60 × 5]> <tibble [1 × 3]>Example #4: hyper-parameter tuning with CV
# look at accuracy for all the models: knn_res |> collect_metrics()
best_k <- knn_res |> select_best(metric = "roc_auc")
best_k# A tibble: 1 × 2
neighbors .config
<int> <chr>
1 20 Preprocessor1_Model20Step 5: Predict